AI is Democratizing Cybercrime: What North Carolina Businesses Need to Know
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer confined to research labs, tech giants, or specialized enterprises. It is accessible, affordable, and, increasingly, weaponized. While businesses in North Carolina are exploring AI to drive innovation and efficiency, malicious actors are exploiting the same technology to lower the barriers of entry into cybercrime. AI is democratizing cybercrime, making advanced attacks available to individuals with minimal technical expertise.
This blog explores how AI is fueling the rise of cybercrime, why North Carolina businesses should pay attention, and how to safeguard against these evolving threats.
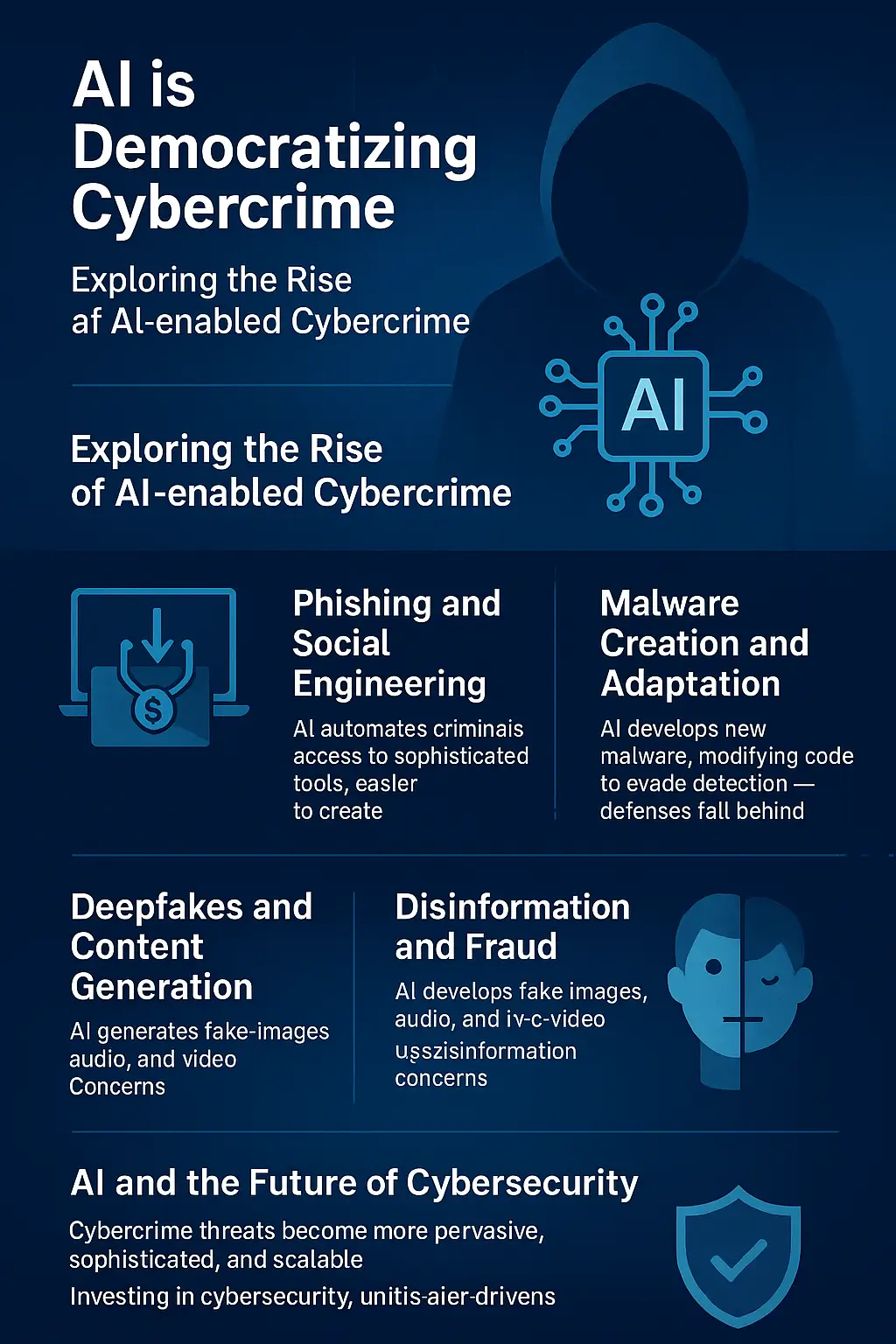
Understanding the Concept: What Does “AI is Democratizing Cybercrime” Mean?
Traditionally, launching cyberattacks required specialized knowledge, coding skills, and significant resources. Today, AI tools—many of them open-source or commercially available—have simplified these processes. Just as AI has democratized innovation for small businesses, it has also democratized cybercrime by lowering the skill threshold needed to conduct attacks.
Examples of AI in Cybercrime:
- AI-powered phishing: Generating emails and text messages indistinguishable from legitimate communications.
- Voice cloning: Mimicking executives’ voices to trick employees in “CEO fraud” scams.
- Automated malware generation: AI models can create new code variations to evade detection.
- Deepfakes: Convincing videos or audio used for fraud, misinformation, or extortion.
For North Carolina businesses, especially small and medium-sized enterprises (SMBs), this shift is concerning. Attacks that once required nation-state resources are now within reach of low-level criminals.
Exploring the Rise of AI-enabled Cybercrime
One of the reasons AI-enabled cybercrime is gaining traction is accessibility. Pretrained AI models are available online, and underground forums now openly discuss and share tools for malicious use.
Key Factors Driving This Rise:
- Open-source availability – Models like GPT, Stable Diffusion, and open-source voice synthesis tools can be repurposed.
- Lower cost – Cloud platforms make computing power affordable, even for malicious users.
- Underground marketplaces – Dark web forums now sell “malware-as-a-service” powered by AI.
- Social engineering enhancement – AI makes phishing, spear-phishing, and impersonation harder to detect.
A 2024 study by the University of California, Berkeley highlights how AI is improving phishing success rates by 80% compared to traditional attacks【source: Berkeley CLTC】.
For North Carolina industries like legal, healthcare, and financial services, which deal with sensitive client data, the implications are serious.
Why North Carolina Businesses Are Prime Targets
North Carolina is home to a growing number of startups, SMBs, and established enterprises, particularly in Raleigh, Durham, Cary, and Charlotte. As these businesses embrace digital transformation, they also increase their exposure to cyber risks.
Specific Risk Areas:
- Healthcare in Durham: AI-generated ransomware targeting hospitals and clinics.
- Financial services in Charlotte: AI-powered fraud detection evasion.
- Legal firms in Raleigh: Deepfake voice calls impersonating clients or partners.
- Manufacturing hubs in Cary and Wake Forest: AI-driven supply chain attacks.
The state’s economic growth makes it an attractive target for cybercriminals who want to exploit organizations unprepared for AI-driven threats.
Case Studies: AI Cybercrime in Action
Case 1: The Deepfake CEO Scam
In 2023, a UK energy firm lost $243,000 after an employee was tricked by a deepfake audio of their CEO. Similar scams could easily target executives in Raleigh or Durham.
Case 2: AI-enhanced Phishing at Scale
A financial services company in the U.S. reported AI-generated phishing emails that bypassed spam filters and tricked employees into revealing login details. For North Carolina banks, the risk of such breaches is enormous.
Case 3: Healthcare Ransomware
Hospitals nationwide are reporting ransomware campaigns powered by AI that automatically adjust tactics based on defenses. In a healthcare-rich region like Durham, this poses a serious public safety threat.
AI and the Future of Cybersecurity
If AI is empowering cybercriminals, it can also empower defenders. AI and the future of cybersecurity are deeply intertwined. Security teams are already leveraging AI to detect anomalies, automate responses, and predict attacks before they occur.
Defensive Applications of AI:
- Threat detection: Machine learning models identify unusual behavior in networks.
- Automated response: AI can isolate infected devices before malware spreads.
- Fraud prevention: Financial institutions use AI to flag suspicious transactions in real-time.
- Phishing detection: AI can analyze emails for subtle indicators of fraud.
The challenge is that cybercriminals evolve just as fast, creating an AI arms race.
Separating Fact from Fiction: Myths About AI in Cybercrime
While the threat is real, it’s important to avoid sensationalism. Fortinet and Harvard cybersecurity experts emphasize that not every AI innovation translates into a major threat【Harvard Extension】【Fortinet Blog】.
Common Myths:
- Myth 1: AI will replace all hackers.
- Reality: AI lowers barriers but still requires human intent and strategy.
- Myth 2: AI makes all attacks undetectable.
- Reality: Strong cybersecurity practices still reduce risks significantly.
- Myth 3: Only large companies are targets.
- Reality: SMBs, especially in North Carolina, are prime targets due to weaker defenses.
Best Practices for North Carolina Businesses
- Invest in AI-driven Cybersecurity Tools
Local businesses should deploy solutions that use AI for anomaly detection, automated monitoring, and endpoint protection.
- Employee Training
Employees remain the weakest link. Regular training on spotting phishing, voice scams, and deepfakes is crucial.
- Collaborate with Managed IT Services Providers
For SMBs in Raleigh, Cary, and Chapel Hill, partnering with IT services providers ensures continuous monitoring and proactive defense.
- Develop Incident Response Plans
Being prepared minimizes damage. Plans should include protocols for ransomware, phishing, and data breaches.
- Stay Updated on Regulatory Requirements
Industries like healthcare and finance must comply with HIPAA, FINRA, and other regulations. Non-compliance can worsen the impact of breaches.
The Ethical Debate: Dual Use of AI
AI’s dual-use nature—being both a weapon and a defense tool—presents a societal challenge. Policies and international cooperation will be necessary to limit misuse without stifling innovation. Organizations like the Carolina Cyber Center and local universities are already exploring frameworks for safe AI adoption.
Looking Ahead: What North Carolina Businesses Should Expect
In the next five years, expect:
- More sophisticated deepfakes targeting executives and politicians.
- AI malware that evolves in real time against defenses.
- Greater regulatory oversight in cybersecurity.
- Expanded collaboration between governments, tech firms, and businesses.
Conclusion
AI is a double-edged sword—while it democratizes innovation for small businesses, it also democratizes cybercrime. For North Carolina’s growing economy, the stakes are high. From Raleigh’s legal firms to Durham’s healthcare systems, every sector must prepare for AI-driven threats.
By investing in AI-enabled cybersecurity, fostering awareness, and partnering with managed IT services, businesses can safeguard their future. The rise of AI-enabled cybercrime is inevitable, but with the right strategy, its impact can be managed and mitigated.

