AI Tools Are Everywhere. Here’s How to Use Them Without Making a Mess.
If you feel like a new AI tool launches every morning before your first cup of coffee, you’re not imagining things.
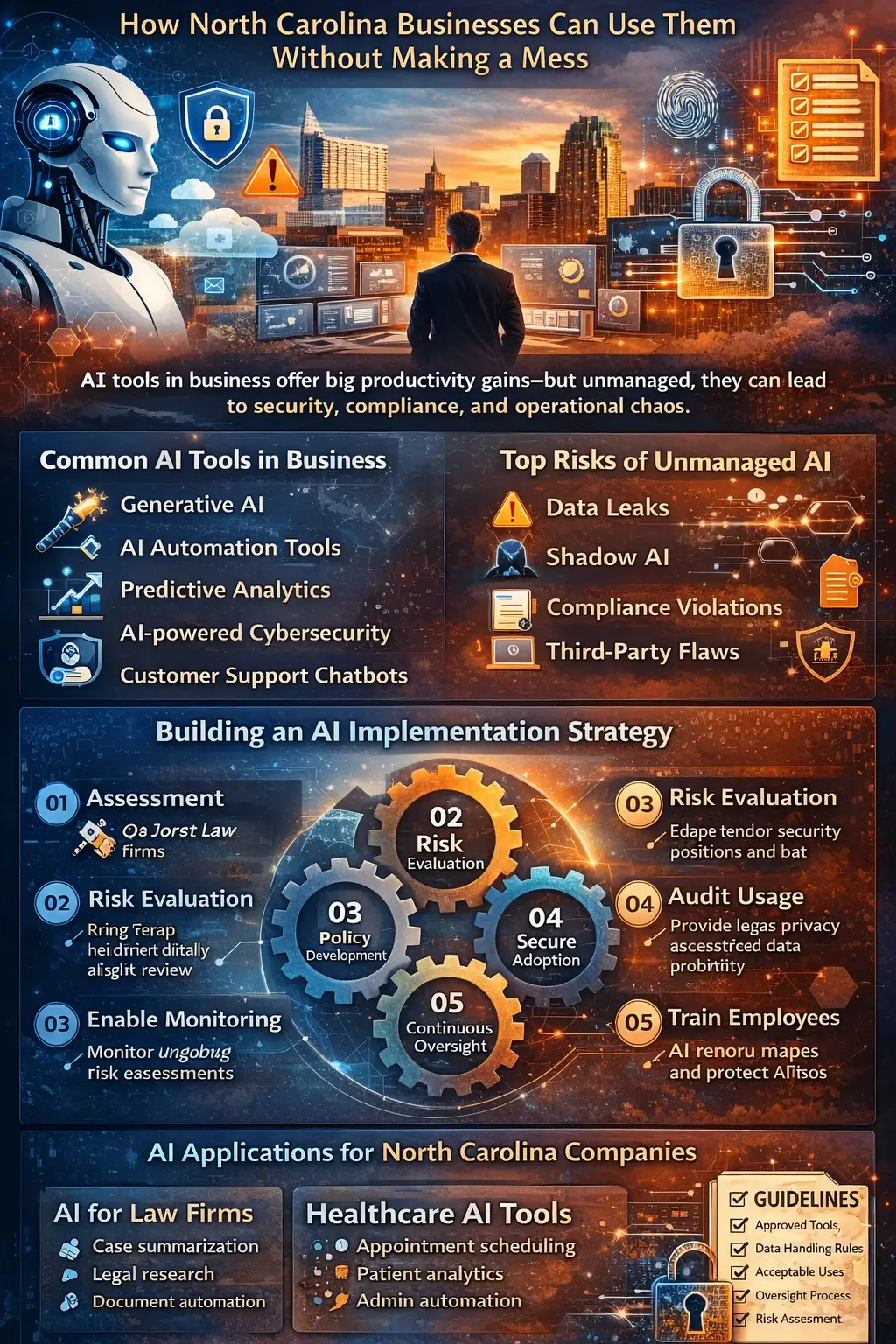
From marketing automation platforms and generative AI writing assistants to customer service chatbots and predictive analytics dashboards, AI tools in business are multiplying at an extraordinary pace. For many North Carolina companies—especially small and mid-sized businesses—this presents both an opportunity and a risk.
The opportunity? Greater efficiency, smarter decisions, and improved productivity.
The risk? Data leaks, compliance violations, operational confusion, and what IT professionals increasingly call Shadow AI.
The truth is this: AI is not the problem. Lack of structure is.
Let’s explore how businesses across Raleigh, Durham, Cary, Wake Forest, and beyond can embrace AI innovation without creating unnecessary chaos.
Why AI Tools Are Ranking Everywhere Online
A quick look at top-ranking articles on this topic reveals a consistent pattern. The content that performs best:
- Addresses AI overload
- Warns about AI security risks
- Mentions Shadow AI
- Highlights the need for governance
- Offers basic best practices
However, many articles remain surface-level. They discuss trends but stop short of offering a detailed AI implementation strategy, particularly for AI tools for small business environments.
This article goes deeper—because businesses in North Carolina need more than warnings. They need structure.
The Explosion of AI Tools in Business
Ten years ago, businesses debated whether to move to the cloud.
Today, the debate is about which AI platform to adopt first.
Common categories of AI productivity tools include:
- Generative AI (content, coding, documentation)
- AI automation tools (workflow, scheduling, CRM triggers)
- Predictive analytics platforms
- AI-powered cybersecurity monitoring
- Customer support chatbots
- AI financial forecasting software
For AI tools for SMBs, these platforms promise enterprise-level capabilities at affordable costs. That is transformative—especially for growing businesses across North Carolina.
But here is where it becomes complicated.
The Hidden Problem: AI Tool Sprawl
Imagine your employees each subscribing to different AI tools:
- Marketing uses one AI writer.
- Sales uses a separate CRM AI plugin.
- HR uses an AI resume screener.
- Accounting uses AI reconciliation software.
- Operations experiments with automation bots.
No coordination. No oversight.
This is called AI tool sprawl—and it’s rapidly becoming a major operational issue.
Without proper AI tool management, organizations face:
- Duplicate subscriptions
- Data silos
- Increased AI cybersecurity risks
- Shadow AI activity
- Inconsistent data policies
- Rising compliance exposure
The technology itself may be impressive. The implementation? Often messy.
Understanding Shadow AI: The Quiet Risk
You may already be dealing with Shadow AI without realizing it.
Shadow AI occurs when employees use AI tools without IT approval or oversight. Often, they do so with good intentions—seeking efficiency or productivity gains.
However, the risks include:
- Uploading sensitive client data into public AI systems
- Violating confidentiality agreements
- Breaching HIPAA, GLBA, or industry regulations
- Increasing AI data leakage risks
- Creating exposure to AI compliance risks
For example:
A small law firm in North Carolina might use generative AI to summarize case documents. If confidential case information is entered into an unsecured platform, the firm could face serious ethical and legal consequences.
Similarly, an accounting firm using AI for financial analysis must ensure AI data protection standards are upheld.
Innovation without governance is exposure.
AI Productivity vs Risk: Striking the Right Balance
AI brings undeniable advantages:
- Faster document creation
- Smarter forecasting
- Automated customer communication
- Streamlined internal processes
But leaders must weigh AI productivity vs risk carefully.
Ask yourself:
- Where is company data being processed?
- Who owns the output generated by AI?
- Are tools compliant with industry regulations?
- Is there a formal AI policy for employees?
Without these safeguards, the productivity boost may be short-lived—and expensive.
AI Security Risks Businesses Cannot Ignore
Let’s be clear: AI tools introduce new threat surfaces.
Common AI security risks include:
- AI Data Leakage Risks
Employees may unintentionally expose proprietary information through AI prompts.
- AI and Ransomware Risks
AI systems integrated into workflows can become attack vectors if improperly secured.
- Third-Party Vulnerabilities
Many AI tools rely on external APIs. Weak vendor security can compromise your environment.
- Compliance Violations
Poor AI compliance management can lead to regulatory fines.
For industries like healthcare, legal services, and financial consulting across North Carolina, these are not theoretical concerns.
AI Governance: The Missing Piece in Most Organizations
The most effective organizations implement a structured AI governance framework.
AI governance ensures:
- Responsible AI usage
- Ethical deployment
- Data protection alignment
- Security oversight
- Regulatory compliance
An effective AI governance strategy typically includes:
- Defined ownership (Who oversees AI use?)
- Approved tool lists
- Risk assessment processes
- Vendor review protocols
- Clear AI usage guidelines
- Monitoring and auditing mechanisms
Without governance, AI adoption becomes reactive instead of strategic.
Building an AI Implementation Strategy for North Carolina Businesses
Whether you’re in Raleigh or Chapel Hill, a structured AI implementation roadmap should follow these phases:
Phase 1: Assessment
- Identify business objectives
- Evaluate operational pain points
- Assess current cybersecurity posture
Phase 2: Risk Evaluation
- Conduct AI risk management review
- Identify compliance obligations
- Evaluate vendor security
Phase 3: Policy Development
- Draft an AI policy template
- Define approved use cases
- Establish data handling protocols
Phase 4: Secure AI Adoption
- Implement technical controls
- Enable monitoring
- Provide employee training
Phase 5: Continuous Oversight
- Audit usage
- Review performance
- Update governance standards
This transforms AI adoption from experimentation into strategic advantage.
AI Tools for Small Business: Practical Examples
Let’s consider how AI applies across common North Carolina industries.
AI for Law Firms
- Document summarization
- Legal research assistance
- Case management automation
Requires strict AI compliance management and confidentiality safeguards.
AI in Healthcare Practices
- Appointment scheduling
- Predictive patient analytics
- Administrative automation
Must align with HIPAA and strong AI data protection policies.
AI for Accounting Firms
- Automated reconciliation
- Fraud detection
- Financial forecasting
Requires oversight of financial data handling.
AI for Professional Services
- CRM optimization
- Client reporting automation
- Workflow tracking
Needs structured governance to avoid data fragmentation.
The technology is powerful—but only if supported by a solid business AI strategy.
Managing AI in the Workplace: Leadership Responsibility
Successful managing AI in the workplace requires leadership involvement.
Executives must:
- Define clear use cases
- Communicate policies
- Provide training
- Monitor adherence
AI should not become an unsupervised experiment.
An internal AI policy for employees should address:
- Approved platforms
- Prohibited data sharing
- Compliance responsibilities
- Reporting procedures
- Disciplinary actions for violations
Structure creates confidence.
Data Privacy and AI: A Growing Concern
Data privacy regulations are evolving rapidly.
Businesses must ensure:
- Data is encrypted
- AI vendors meet compliance standards
- Personally identifiable information (PII) is protected
- Client confidentiality remains intact
Ignoring data privacy and AI risks can lead to severe financial and reputational damage.
Secure AI adoption is not optional—it is essential.
AI Automation Tools: Enhancing Operations Without Chaos
AI automation tools can significantly improve:
- Workflow efficiency
- Customer experience
- Inventory tracking
- Financial reporting
- Internal communication
However, automation should follow strategic review—not impulse adoption.
This is where AI best practices for businesses matter.
Best practices include:
- Pilot testing before full deployment
- IT approval before tool adoption
- Role-based access control
- Continuous monitoring
AI should simplify operations—not complicate them.
The Role of Managed IT Support for AI
For many small and mid-sized businesses, internal IT teams are already stretched thin.
This is why managed IT support for AI is becoming increasingly valuable across North Carolina.
A qualified IT partner can assist with:
- AI vendor vetting
- Risk assessments
- AI cybersecurity risk evaluation
- Policy development
- Ongoing monitoring
- Compliance alignment
AI should align with your broader IT and cybersecurity strategy—not operate independently.
Responsible AI Usage: The Long-Term Perspective
AI adoption is not a short-term trend. It is a permanent shift in how businesses operate.
Responsible AI usage ensures:
- Ethical decision-making
- Bias mitigation
- Security alignment
- Sustainable productivity gains
The companies that succeed will not be those who adopt the most AI tools—but those who adopt them wisely.
AI Tools for Growing Businesses in North Carolina
From startups in Durham to established firms in Raleigh, AI tools for growing businesses can accelerate expansion.
But growth requires stability.
A structured AI implementation strategy ensures:
- Reduced operational friction
- Lower security exposure
- Improved compliance readiness
- Sustainable efficiency gains
AI should support growth—not create preventable setbacks.
Final Thoughts: Innovation Requires Discipline
AI tools are powerful. They can transform operations, improve productivity, and help small businesses compete at enterprise levels.
But without:
- AI governance
- AI risk management
- Secure AI adoption
- Compliance oversight
You risk turning opportunity into disorder.
The path forward is not fear—it is structure.
Businesses across North Carolina that implement AI thoughtfully, strategically, and securely will lead the next decade of innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are the biggest AI security risks for small businesses?
The most significant AI security risks include data leakage, Shadow AI usage, compliance violations, and vendor vulnerabilities. Without structured AI governance, these risks increase significantly.
- What is Shadow AI?
Shadow AI refers to employees using AI tools without IT approval. This can lead to data exposure, compliance risks, and cybersecurity vulnerabilities.
- Do small businesses need an AI governance framework?
Yes. Even small businesses using AI tools for SMBs need an AI governance framework to manage risk, ensure compliance, and protect data.
- How can businesses ensure secure AI adoption?
Secure AI adoption requires risk assessment, vendor evaluation, employee policies, monitoring, and alignment with cybersecurity best practices.
- Should AI be part of a broader business AI strategy?
Absolutely. AI implementation should align with overall IT, cybersecurity, and operational goals—not function independently.

