The Jaguar Land Rover Cyberattack: Lessons for Businesses on Cybersecurity and Supply Chain Resilience
In September 2025, Jaguar Land Rover (JLR)—one of the world’s most iconic automakers—faced a crippling cyberattack that brought production lines to a halt and sent shockwaves through global supply chains. What began as a highly technical breach quickly escalated into a corporate and economic crisis, leaving suppliers, dealers, and even governments scrambling to assess the fallout.
For businesses in North Carolina, this story may feel distant—taking place in the United Kingdom with a European carmaker. But the lessons from this attack are highly relevant. Whether you run a small law firm in Raleigh, manage a healthcare practice in Durham, or oversee a manufacturing facility in Cary, the JLR cyberattack underscores a reality that no modern business can ignore: cybersecurity is not just an IT problem—it’s a business survival issue.
The attack on JLR highlights how vulnerable even the largest, best-resourced companies are to sophisticated digital threats. If a global automaker with thousands of employees and a vast IT budget can be brought to its knees, smaller organizations without the same level of protection must pay even closer attention. In North Carolina, where industries from biotech to automotive parts manufacturing depend on reliable IT systems, the lessons are crystal clear: preparedness is everything.
What Happened: The JLR Cyberattack Timeline
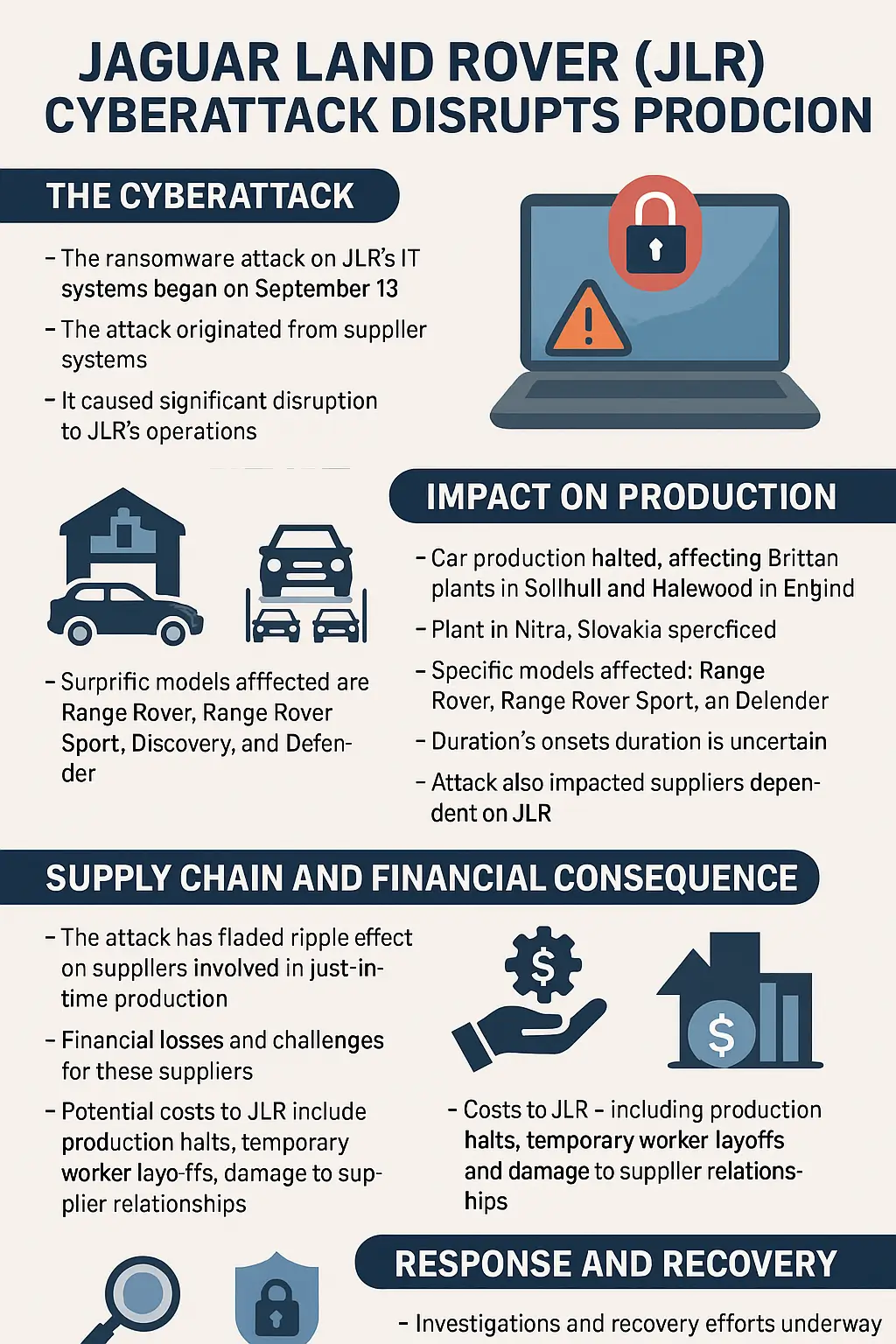
The Jaguar Land Rover cyberattack was first reported in mid-September 2025. Initial news confirmed that the company had experienced a ransomware attack that forced it to suspend production at several UK plants. Investigations suggested the attackers exploited vulnerabilities in JLR’s IT infrastructure, crippling its ability to manage logistics, supplier communications, and production systems.
The disruption wasn’t short-lived. While JLR initially hoped to resume operations quickly, reports from Wired and The Guardian revealed that the shutdown extended for weeks. Suppliers across Europe began warning of long-term consequences, with some estimating disruptions “well beyond Christmas.” Thousands of employees were left idle, and dealers faced significant backlogs in fulfilling customer orders.
What made the situation even worse was its ripple effect. JLR is at the center of a vast supply chain, working with hundreds of suppliers for everything from raw materials to specialized components. When the company stopped production, many of these suppliers also faced halted orders, lost revenue, and mounting uncertainty.
In many ways, this was a classic supply chain domino effect. When one major player falls, every dependent partner in the network feels the impact. This makes the JLR cyberattack more than just a “company issue”—it became a cautionary tale for global industries, showing how interconnected and fragile today’s digital supply chains truly are.
How the Attack Disrupted Operations
The Jaguar Land Rover (JLR) cyberattack wasn’t just a temporary inconvenience—it was a full-scale disruption that paralyzed critical aspects of the company’s operations. Production lines in multiple UK facilities, including key plants in Solihull and Halewood, were forced to shut down. Employees who typically worked around the clock assembling Range Rovers, Defenders, and other luxury vehicles were suddenly left idle, waiting for IT systems to come back online.
Industry analysts compared the event to “pulling the plug on a factory’s power supply.” Without functioning IT systems, JLR couldn’t process supplier data, schedule assembly tasks, or manage shipments. Even routine tasks like inventory tracking or coordinating logistics became impossible.
One striking detail reported by The Times was how quickly suppliers began to feel the strain. Businesses that had invested heavily in production for JLR’s high-demand models found themselves sitting on inventory with no immediate buyer. For smaller suppliers, some of whom rely on JLR for the majority of their contracts, the shutdown posed an existential threat.
This isn’t just about lost time—it’s about lost trust. Customers waiting for vehicles faced indefinite delays, dealers couldn’t provide firm delivery estimates, and suppliers were forced to pause production, creating bottlenecks that will take months to untangle.
The Supply Chain Fallout
What makes the JLR cyberattack particularly alarming is its cascading effect on the wider supply chain. In today’s global economy, few companies operate in isolation. JLR’s halted operations didn’t just impact its own bottom line—they rippled outward to hundreds of other companies, big and small.
Think of it like a row of dominoes. JLR, as one of the world’s largest luxury automakers, is the first domino. When it toppled under the weight of a cyberattack, the impact spread instantly through its suppliers, dealers, and even international partners.
- Suppliers: Companies providing everything from specialized parts to raw materials suddenly had nowhere to send their products. Many of these suppliers run on thin margins and rely on steady production schedules. A prolonged disruption could mean layoffs, missed revenue, or even bankruptcy.
- Dealers: Across Europe and beyond, dealerships struggled to explain to customers why vehicles couldn’t be delivered. In the luxury car market, where reputation and reliability are everything, this kind of uncertainty damages consumer trust.
- Logistics providers: Shipping companies that normally handle the flow of parts and vehicles were left with empty schedules, leading to wasted capacity and financial losses.
For businesses in North Carolina, the lesson is sobering. While JLR’s cyberattack may have happened an ocean away, local companies are not immune to similar supply chain vulnerabilities. Many NC manufacturers operate under the just-in-time (JIT) model, where parts arrive only as needed to reduce storage costs. While efficient, this model leaves little room for error. If one key supplier is disrupted—whether due to a cyberattack, natural disaster, or financial collapse—the entire chain grinds to a halt.
A strong comparison can be made with the Colonial Pipeline cyberattack of 2021, which caused widespread fuel shortages across the East Coast, including North Carolina. Just as fuel stations experienced empty pumps in a matter of days, JLR’s suppliers found themselves with empty order books after the attack. Both examples highlight a single truth: cyberattacks don’t just hit servers—they hit people, businesses, and entire economies.
Cybersecurity Weaknesses in the Manufacturing and Automotive Sectors
The Jaguar Land Rover (JLR) cyberattack wasn’t just a one-off incident—it exposed a deep and troubling truth: the manufacturing and automotive sectors are especially vulnerable to cyber threats. Unlike technology companies or financial institutions, which have invested heavily in digital security over the past two decades, many manufacturing firms are still catching up.
Why Manufacturing Is a Target
- Legacy Systems: Many automakers, including JLR, depend on IT systems and production technologies that were never designed to withstand modern cyber threats. Outdated software, unpatched vulnerabilities, and reliance on legacy infrastructure create fertile ground for attackers.
- Interconnected Operations: Factories today are digital ecosystems. Industrial control systems (ICS), robotic assembly lines, and supply chain platforms are tightly connected. While this boosts efficiency, it also means that one breach can ripple across multiple systems.
- High Stakes, Low Tolerance: In manufacturing, downtime is measured in millions of dollars per day. This makes companies more likely to pay ransoms, which in turn makes them attractive targets for cybercriminals.
- Third-Party Dependencies: The reliance on a web of suppliers, contractors, and logistics partners expands the attack surface. A single weak link can open the door to a much larger breach.
The Automotive Industry Under Siege
Automakers have become a favorite target for ransomware groups. Beyond JLR, companies like Toyota and Honda have also experienced production disruptions from cyber incidents. With vehicles becoming increasingly connected—featuring onboard computers, internet access, and even autonomous driving capabilities—the line between IT security and product safety is blurring.
For example, in 2022, Toyota temporarily shut down 14 plants in Japan after a supplier suffered a cyberattack. The cost of just one day of downtime was estimated at over $375 million. JLR’s attack is part of this broader pattern, showing how cybercriminals are systematically exploiting industries that can least afford interruptions.
Comparisons: Past Global Cyberattacks
The JLR incident isn’t happening in isolation—it belongs to a troubling lineage of large-scale cyberattacks that reveal how fragile our digital world can be.
NotPetya (2017)
One of the most devastating cyberattacks in history, NotPetya began as a targeted strike on Ukrainian infrastructure but quickly spread worldwide. Multinational corporations like Maersk (shipping) and FedEx suffered billions in damages. For Maersk, the attack shut down ports and disrupted global trade routes. The lesson? A single piece of malicious code can have worldwide consequences.
Colonial Pipeline (2021)
Closer to home, North Carolina residents remember the Colonial Pipeline attack vividly. A ransomware strike forced the company to shut down its pipeline, which supplies nearly half of the East Coast’s fuel. Panic buying ensued, gas stations ran dry, and businesses were left scrambling. What happened in JLR’s UK factories echoes this event: when a critical system falls, it cascades into daily life for millions.
WannaCry (2017)
Another high-profile ransomware attack, WannaCry crippled healthcare systems, governments, and corporations worldwide. Hospitals in the UK’s National Health Service (NHS) were forced to cancel surgeries and redirect patients. The parallels with JLR are stark: when essential systems become inaccessible, the impact goes far beyond IT—it disrupts lives and livelihoods.
A Digital Hurricane Analogy
Cyberattacks today can be compared to hurricanes. Just as a Category 5 storm can devastate communities, a well-orchestrated cyberattack can level businesses, industries, and economies. And much like hurricane season, cyberattacks are no longer a matter of “if” but “when.”
The difference? While we cannot prevent hurricanes, we can take active steps to prevent or minimize the damage from cyberattacks. JLR’s situation is a reminder that cyber resilience—like storm preparedness—must be a core part of every organization’s strategy.
Why North Carolina Businesses Should Pay Attention
At first glance, a cyberattack on a UK automaker may seem like a problem far removed from the day-to-day concerns of businesses in North Carolina. But in a world where economies are tightly interconnected, what happens in Birmingham or Solihull can quickly ripple across the Atlantic and land in Raleigh, Durham, or Charlotte.
North Carolina’s Growing Manufacturing Hub
North Carolina is rapidly becoming a hub for advanced manufacturing and automotive innovation. With major projects like Toyota’s $13.9 billion battery plant in Randolph County and Vietnamese automaker VinFast’s EV facility in Chatham County, the state is positioning itself as a cornerstone of the next generation of transportation. But as these industries grow, so too does their exposure to cyber threats.
If Jaguar Land Rover—a company with decades of experience and significant IT investments—can be disrupted, the same vulnerabilities exist for emerging plants in NC. A ransomware attack on a new EV manufacturer in the state could have devastating consequences, not just for the company but for employees, suppliers, and the broader economy.
The Broader Business Landscape in NC
It’s not just manufacturers who need to be concerned. North Carolina is home to thriving sectors in healthcare, legal services, finance, and education—all industries that rely heavily on technology and sensitive data. A law firm in Raleigh handling confidential client information, or a healthcare practice in Durham storing patient records, faces similar risks. A single cyberattack could compromise their reputation, disrupt operations, and expose them to costly legal liabilities.
Lessons from JLR for NC Businesses
The JLR cyberattack underscores that size doesn’t guarantee safety. Whether you’re a global automaker or a small local business, the same principles apply: cyber threats are real, and resilience requires proactive planning. For North Carolina businesses, now is the time to evaluate your cyber defenses, revisit incident response plans, and ensure your vendors and partners are equally vigilant.
Cybersecurity Lessons for Businesses
So, what can companies in North Carolina learn from Jaguar Land Rover’s misfortune? Here are some practical takeaways that apply across industries:
- Vendor Risk Management
JLR’s attack highlighted the dangers of supply chain vulnerabilities. For NC businesses, this means you can’t just secure your own systems—you must also evaluate the cybersecurity practices of your vendors, contractors, and partners. One weak link in your supply chain can put your entire business at risk.
- Proactive Monitoring and Detection
Ransomware groups thrive on stealth. By the time a breach is detected, attackers may have already stolen data or locked critical systems. Investing in proactive monitoring, intrusion detection systems, and 24/7 threat response can significantly reduce the damage.
- Zero Trust Approach
Gone are the days when a firewall alone could protect a network. Modern businesses need to adopt a Zero Trust model, which assumes that no user or system is automatically trustworthy. Every access request should be verified, every connection monitored.
- Employee Awareness Training
Many cyberattacks start with something as simple as a phishing email. Training employees to recognize suspicious messages, avoid clicking unknown links, and report unusual activity is one of the most cost-effective defenses available.
- Regular Backups and Recovery Plans
One of the most effective defenses against ransomware is having reliable, secure backups. If your systems are compromised, backups allow you to restore operations without paying a ransom. The key is ensuring backups are tested, up to date, and stored separately from primary systems.
- Incident Response Preparedness
A crisis isn’t the time to start planning your response. Just as companies conduct fire drills, NC businesses should conduct cyber drills—simulated attacks that test response times, communication plans, and recovery processes. The faster you can contain an incident, the less damage it causes.
- Partner with Managed IT Services
For many small and mid-sized businesses in North Carolina, building an in-house cybersecurity team isn’t realistic. Partnering with a managed IT services provider offers access to advanced tools, expert monitoring, and rapid incident response—all without the overhead of a full internal team.
How Managed IT Services in North Carolina Can Help
The Jaguar Land Rover cyberattack makes one thing clear: even the most established companies can be brought to a standstill without strong cyber defenses. For small and mid-sized businesses in North Carolina, the risks are even greater—limited resources often mean less sophisticated defenses, leaving them vulnerable to attack.
This is where Managed IT Services come in. By outsourcing IT management and cybersecurity to a trusted local provider, NC businesses can benefit from enterprise-grade protection without the cost of maintaining a large in-house team.
Key Benefits of Managed IT Services:
- 24/7 Monitoring and Support: Cyberattacks don’t follow business hours. Continuous monitoring ensures threats are detected and neutralized before they escalate.
- Proactive Security Measures: Managed service providers implement firewalls, intrusion detection, endpoint protection, and advanced threat intelligence to keep systems secure.
- Regular Patching and Updates: Outdated software is a hacker’s playground. A managed IT team ensures every system is updated with the latest security patches.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery: In the event of an attack, reliable backups and recovery protocols minimize downtime and prevent data loss.
- Scalability: Whether you’re a growing startup in Chapel Hill or an established manufacturer in Cary, managed IT services adapt to your evolving needs.
For North Carolina businesses, partnering with a provider like Computerbilities means having peace of mind that your IT infrastructure and sensitive data are protected against the unexpected.
Cybersecurity Best Practices Every Business Should Apply
While managed IT services provide the expertise and tools, every business must also adopt strong internal practices to build resilience. Here are best practices that apply to organizations of all sizes:
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adding an extra layer of protection to logins reduces the risk of stolen credentials leading to a breach.
- Segment Networks: Separating critical systems from less sensitive areas of your network limits the spread of malware.
- Encrypt Data: Both in transit and at rest, encryption ensures stolen data is useless to attackers.
- Conduct Regular Audits: Routine cybersecurity audits identify vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
- Develop a Culture of Security: Encourage employees to treat cybersecurity as part of their job, not just IT’s responsibility.
These steps, when combined with professional IT support, create a layered defense that makes it far harder for attackers to succeed.
The Future of Cybersecurity in Manufacturing and Beyond
The JLR cyberattack is not the last of its kind. In fact, experts predict that ransomware attacks, supply chain breaches, and AI-driven cybercrime will only grow in scale and sophistication. Governments are responding with new regulations, while businesses are being pushed to invest more heavily in digital defenses.
For manufacturers in particular, the convergence of IT (information technology) and OT (operational technology) is creating new risks. As factories become smarter and more connected, the attack surface expands. The challenge for businesses in North Carolina is to stay ahead of these evolving threats, not just react after the damage is done.
The future belongs to organizations that treat cybersecurity as a strategic priority, not an afterthought. Those who invest in resilience will not only survive digital disruptions but thrive in a competitive marketplace.
Lessons from the Jaguar Land Rover Cyberattack
The Jaguar Land Rover cyberattack serves as a stark reminder that no company—regardless of size, industry, or reputation—is immune to cyber threats. It disrupted production, strained supply chains, and eroded customer trust, all because of a single breach in digital defenses.
For North Carolina businesses, the lesson is simple: act now, not later. Whether you’re in manufacturing, healthcare, legal services, or any other sector, cybersecurity is central to your survival and growth.
This is where Computerbilities comes in. As a trusted IT support and IT services provider, Computerbilities helps businesses strengthen their defenses, protect sensitive data, and ensure uninterrupted operations. With proactive monitoring, advanced cybersecurity tools, and personalized support, Computerbilities empowers local organizations to face the future with confidence.
In today’s world, a cyberattack is not a question of if, but when. The real question is: will your business be ready?

